
Using Simple Salts to Produce Safer Electrolytes for Aqueous Batteries
A team of Russian scientists including HSE MIEM researchers have used superconcentrated salt solutions to produce effective water-based electrolytes that demonstrate high conductivity and electrochemical stability and require lower amounts of non-toxic salts, making the batteries safer and less expensive than classical non-aqueous ones. The study is published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
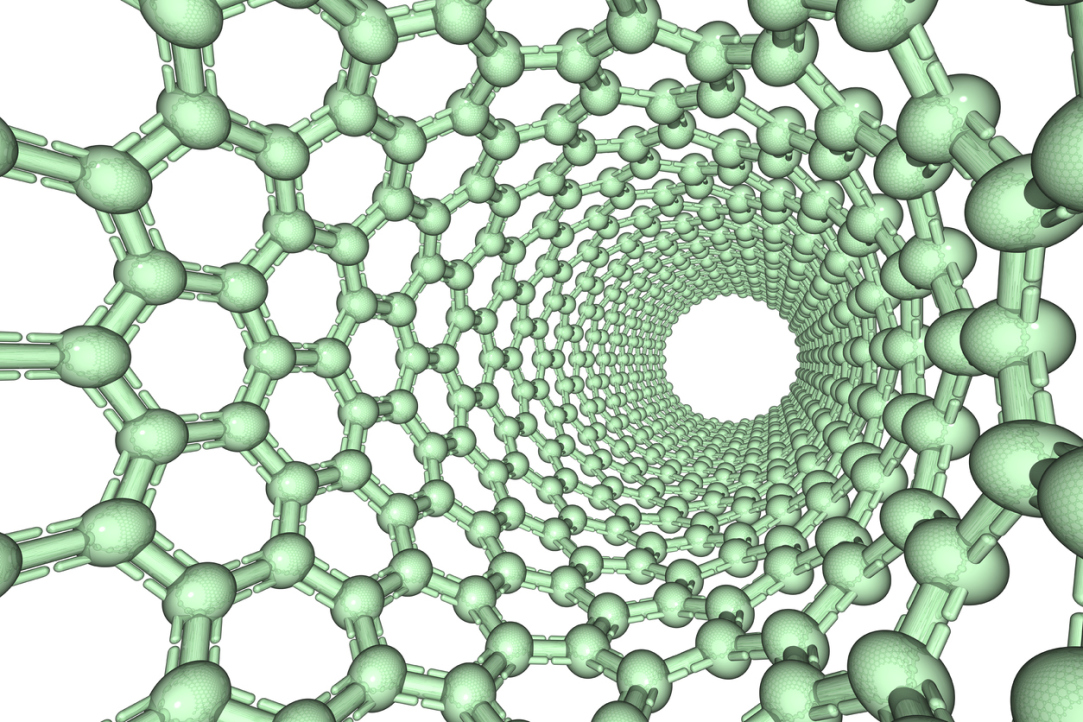
Tunnelling Contact Helps to Study Electron Structure of Carbon Nanotubes
Russian physicists have demonstrated how tunnelling contacts can be used for single-particle states spectroscopy in carbon nanotubes. The proposed technology of tunnelling contact fabrication and the spectroscopic method will help measure the exact nanotube bandgap value, which is the key characteristic required for design of any nanotubes-based electronic devices. Applied Physics Letters publishes the result of the study.

Researchers Compare Energy Consumption During Extraction and Synthesis of One Diamond Carat
Researchers from HSE University, RAS, and Skoltech have compared actual specific energy consumption in the production of diamonds using traditional (mining) and innovative (synthesis) methods. Depending on the technology, 36 to 215 kWh of energy is consumed to produce a 1 carat diamond. It turned out that not all diamond synthesis technologies surpass extraction methods in terms of energy efficiency. The results of the study were published in the journal Energies.

Researchers Begin to Understand Correlation of Schumann Resonances and Dust Storms on Mars
The interaction of dust particles in Martian dust storms may cause electric fields that are powerful enough to have charges that induce standing electromagnetic waves known as Sсhumann resonances. This is the conclusion drawn by physicists from HSE University, the Space Research Institute, and MIPT. The paper was published in Icarus journal.

Statistical Physics Can Help Uncover the Impact of Media on Decision Making
Students and researchers from HSE University and the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics have examined the widely known ‘Prisoner’s Dilemma’ game using methods from statistical physics. They used the mean-field concept, a common tool for studying the physics of many-particle systems, to describe human decision-making processes. Researchers suggest that this model may be helpful for understanding systems with many participants. The results of the study are published in the September issue of the Physics Review Research journal.
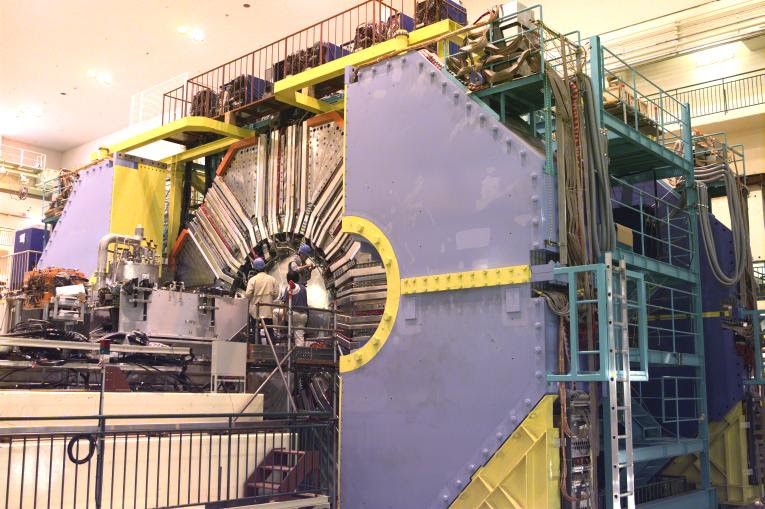
Scholars Gain New Data on Heavy Exotic Hadrons
As part of the Belle experiment, researchers were able to measure the energy dependence of e+e- -> B-anti-B, B-anti-B* and B*-anti-B* reactions in the 10.63 GeV to 11.02 GeV energy range for the first time. The new data will help clarify the nature of the group of exotic Upsilon mesons that have mass in this range. The results of the study were published in the Journal of High Energy Physics.
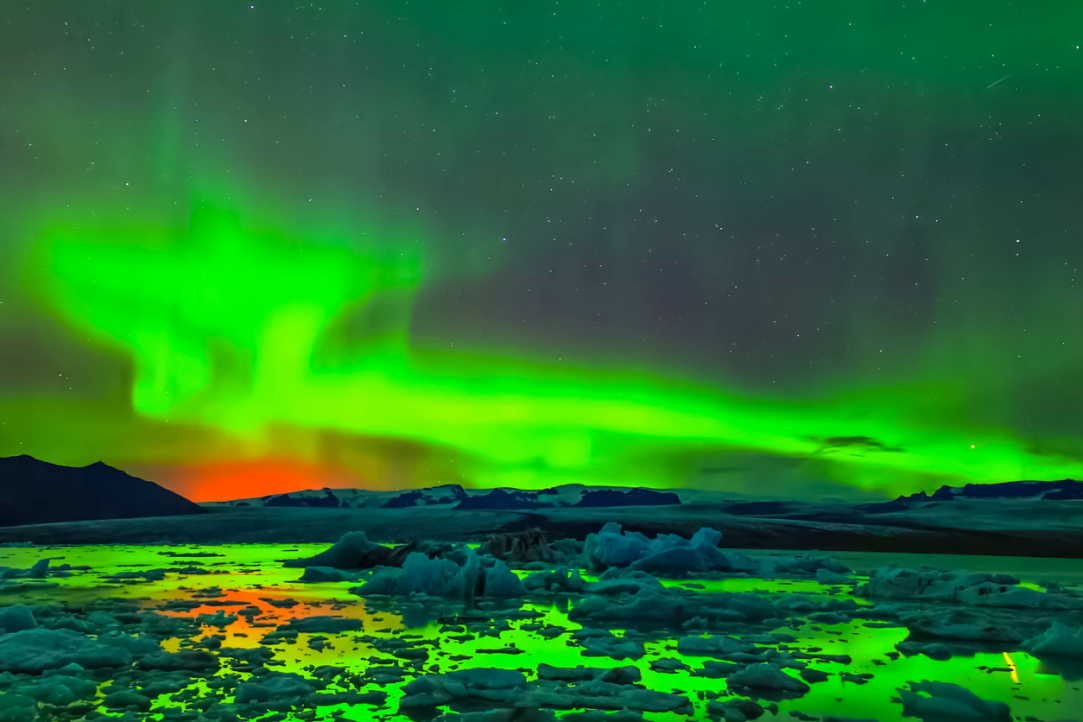

Researchers Explain Potential Cause of Earth’s Green Airglow
A team of Russian researchers from HSE University, the Russian Space Research Institute, and the Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial Magnetism (Russian Academy of Sciences) has described the development of modulational instability of electromagnetic waves in dusty ionospheric plasma, which is caused by a high intensity of electromagnetic emissions. The researchers considered inelastic collisions of ionospheric plasma particles and formulated new tasks and applications to be addressed at a later stage. The results are published in the Physics of Plasmas journal.
Russian Researchers Obtain New Data on Solar Magnetic Field Asymmetry
Researchers from the Institute of Earthquake Prediction Theory and Mathematical Geophysics (Russian Academy of Science) and HSE University have proven that asymmetry between meridional flows in the northern and southern hemispheres of the Sun depends on the anomalies of the solar magnetic field. Research undertaken by Elena Blanter and Mikhail Snirman reveals new aspects of the importance of solar magnetic field asymmetry for predicting the anomalies of the Sun’s activity. The article has been published in Solar Physics.
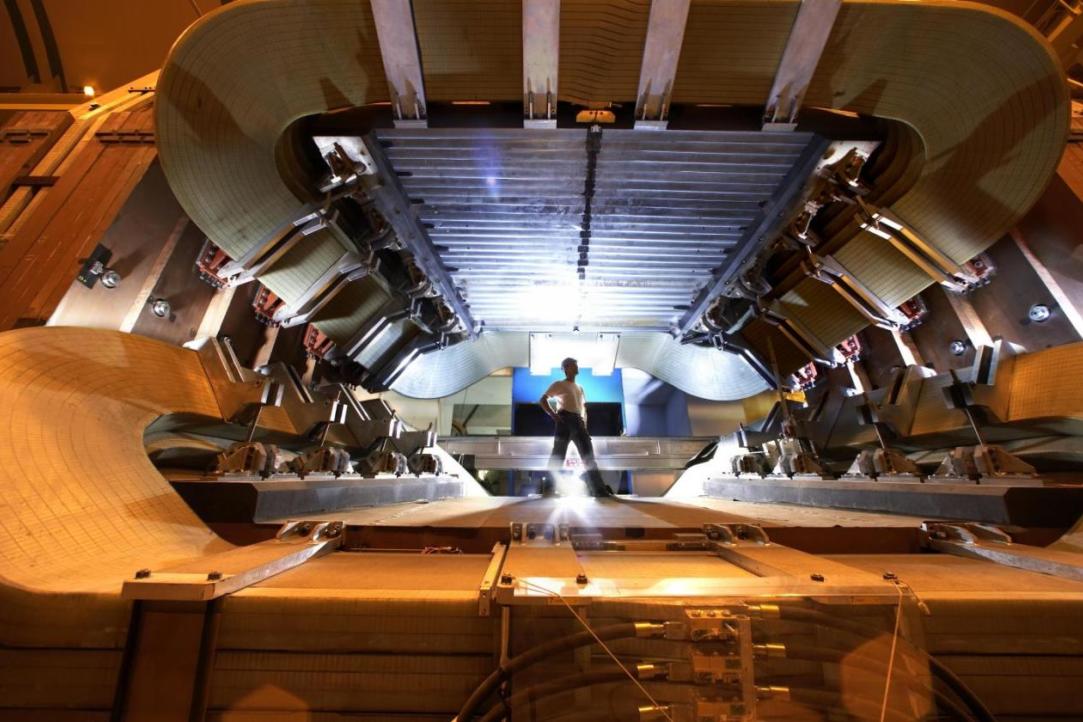

Charmed, Doubly Strange
LHCb (Large Hadron Collider beauty) collaboration, one of the LHC (Large Hadron Collider) experiments, reported that their detector has identified particles that have not previously been detected in physics experimentally – excited omega baryons (Ω-b). Just several years ago, detecting such particles in LHC was believed to be next to impossible. Among proton particles, the excited ‘charmed omegas’ were preselected by an algorithm created by staff from the HSE Laboratory of Methods for Big Data Analysis and Yandex LLC. IQ.HSE talked to Denis Derkach and Fedor Ratnikov about their collaboration’s ‘fresh catch’ and about the point of ‘fishing’ on LHCb in general.

‘A Physicist Has to Be a Romantic’
Alexey Starobinsky, a professor of physics at HSE University and a fellow at the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics at the Russian Academy of Science, has been awarded the Dirac Medal of the ICTP, a prestigious prize awarded annually by the Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical Physics. HSE News Service spoke with the laureate about his path to international recognition, his students, and the award.


Deadline for applications to present academic reports - January 20, 2025